Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) are an important policy tool aimed at promoting the use of renewable energy sources and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This article will delve deep into the concept of RPS, exploring its significance, implementation and impact on the energy sector.
What Are Renewable Portfolio Standards?
Renewable Portfolio Standards, also known as Renewable Energy Standards (RES), are regulatory policies that mandate or encourage utilities to obtain a certain percentage of their energy from renewable sources. These standards are typically set by state governments or regional authorities and serve as a mechanism to promote the adoption of renewable energy technologies.
The Significance of RPS
RPS programs play a vital role in accelerating the development and deployment of renewable energy resources. By setting targets for renewable energy generation, RPS policies create a predictable market demand for clean energy. This, in turn, encourages investment in renewable energy projects, stimulates innovation, and drives down costs over time.
- Promoting Renewable Energy: RPS policies are designed to increase the share of renewable energy in a region’s total energy mix. By setting specific targets, governments ensure that utility companies invest in renewable energy projects, such as wind farms, solar power plants, and hydroelectric facilities. This not only reduces dependence on finite fossil fuels but also mitigates the environmental impact associated with traditional energy generation.
- Economic Benefits: RPS policies stimulate the growth of the renewable energy industry, leading to job creation and economic development. Investments in renewable energy projects create a demand for skilled labor, from engineering and construction to operation and maintenance. Moreover, the renewable energy sector attracts private investments, fostering innovation and technological advancements.
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Renewable energy sources produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels. By increasing the deployment of renewables through RPS policies, governments contribute to global efforts in combating climate change. The reduction in carbon dioxide and other harmful emissions helps mitigate the adverse effects of greenhouse gases on the environment and public health.
Implementing RPS
The implementation of Renewable Portfolio Standards involves several key steps:
- Setting Targets: Governments establish specific renewable energy targets to be achieved by utility companies within a defined timeframe. These targets are often expressed as a percentage of the total energy consumption or generation.
- Compliance Mechanisms: Regulatory frameworks are put in place to ensure compliance with the established targets. Utility companies are required to submit periodic reports on their renewable energy procurement and demonstrate progress towards meeting the set standards.
- Renewable Energy Credits (RECs): To facilitate compliance, Renewable Energy Credits are often used. RECs represent the environmental attributes of renewable energy generation and can be bought, sold, or traded. Utility companies can purchase RECs from renewable energy producers to meet their RPS obligations.
- Penalties and Incentives: Governments may impose penalties on utility companies that fail to meet the RPS targets. On the other hand, incentives such as tax credits, grants, and subsidies are provided to encourage investments in renewable energy projects.
Read: How are Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) Valued?
State-Level Implementation
RPS policies are primarily implemented at the state level, with each state having its own specific targets and requirements. States have the flexibility to tailor their RPS programs to suit their unique energy needs, available resources, and political landscape. This decentralized approach allows for experimentation and innovation, fostering competition among states to achieve higher levels of renewable energy penetration.
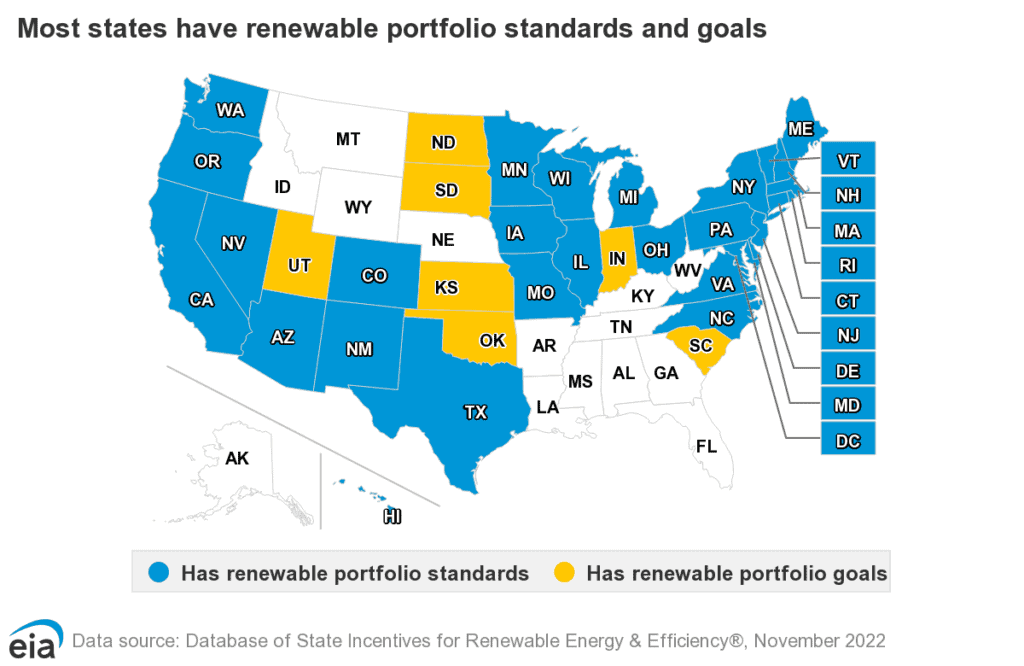
Compliance Mechanisms
To ensure compliance with RPS requirements, states employ various mechanisms. One common approach is the use of Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) or Renewable Energy Certificates. RECs represent the environmental attributes of one megawatt-hour (MWh) of renewable energy generation and can be traded among utilities to meet their RPS obligations. Alternatively, some states may impose fines or penalties for non-compliance.
Interconnection and Grid Integration
As renewable energy sources are integrated into the electricity grid, ensuring smooth interconnection and grid reliability becomes crucial. States with RPS programs often develop interconnection standards and grid integration policies to facilitate the seamless integration of renewable energy projects. These policies help streamline the process for connecting renewable energy systems to the grid and promote efficient transmission of clean power.
Impact of RPS on the Energy Sector
RPS policies have had a profound impact on the energy sector, driving significant growth in renewable energy capacity and transforming the electricity generation mix. Here are some key effects of RPS implementation:
- Increased Renewable Energy Deployment: RPS programs have been instrumental in increasing the deployment of renewable energy technologies, such as wind, solar, geothermal, and biomass. By providing a market-driven incentive for utilities to procure renewable energy, RPS policies have led to a substantial expansion of clean energy capacity across the United States.
- Economic Growth and Job Creation: The renewable energy sector has become a major source of economic growth and job creation. RPS policies stimulate investment in renewable energy projects, leading to the development of new manufacturing facilities, installation jobs, and operations and maintenance positions. This not only helps reduce unemployment but also fosters local economic development.
- Carbon Emission Reductions: One of the primary motivations behind RPS implementation is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change. By displacing fossil fuel-based generation with renewable energy, RPS policies contribute to substantial reductions in carbon dioxide and other harmful pollutants.
- Energy Independence and Security: RPS programs enhance energy independence and security by diversifying the energy mix and reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. By promoting domestic renewable energy resources, states can reduce their vulnerability to price volatility in global energy markets and increase their energy self-sufficiency.
Read: Tax Credits Available for Solar Energy Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
Renewable Portfolio Standards are instrumental in driving the transition to a clean and sustainable energy future. By mandating or incentivizing utilities to procure a certain percentage of their energy from renewable sources, RPS policies stimulate renewable energy deployment, create economic opportunities, and contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change and energy security, RPS will remain a crucial policy tool for accelerating the adoption of renewable energy technologies.
Interested in renewable energy?
With the ongoing global push towards sustainable energy and incentives increasing domestically, now is an ideal time to invest in renewable energy developments. Partnering with EnergyLink will help ease the complicated navigation of development, construction and financing for your renewable energy project. As a certified National Energy Service Company, we offer a range of financial modeling and project funding opportunities to help your organization achieve its renewable energy goals.
To get started, click here or speak directly with a member of our knowledgeable team by dialing (866) 218-0380. Want to stay up-to-date on the latest energy industry news? Subscribe to our bi-weekly digital newsletter below.






